Goal Structuring Notation is an argumentation notation developed at the University of York. Further details about GSN can be found on the GSN Working Group website.
ASCE is the most widely used commercial tool for GSN.
As described in an article on the Safety Engineering Resource website, the purpose of a goal structure in GSN is:
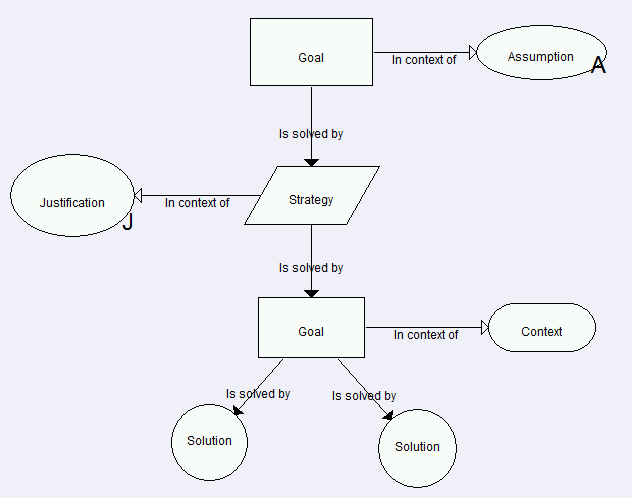
The principal purpose of a goal structure is to show how goals (claims about the system) are successively broken down into ("solved by") sub-goals until a point is reached where claims can be supported by direct reference to available evidence (solutions). As part of this decomposition, using the notation it is also possible to make clear the argument strategies adopted (e.g. adopting a quantitative or qualitative approach), the rationale for the approach and the context in which goals are stated (e.g. the system scope or the assumed operational role).
The principal node types in GSN are as follows:
| Node types | Description |
Goal - a statement or claim asserted within the argument that can be assessed to be true or false, e.g.
|
Each goal (claim) is supported (solved) by a number of sub goals, strategies or solutions. |
Strategy - a description of the argument approach presented in support of a goal. e.g.:
|
This element is optional, but often it is good practice to include to explain the approach to satisfying the parent claim.
If the approach to solving a goal is straightforward or well understood by the intended audience, it is permissible to simply link directly to the supporting goal. |
Solution - a reference to the evidence being presented in support of the goal or strategy, e.g.
|
Usually the solution node will summarise and link out to the relevant report containing the evidence.
ASCE contains a number of tools to support:
|
| Context - Contextual material to define terms used, or the operational context for the system being argued for | |
| Assumption - A supporting proposition that does not have support in this argument | Explicit assumptions can be used to indicate uncertainty or where the scope resolution for some claim is addressed by another party. |
| Justification - A reason or justification that the adopted strategy is being adopted | For example, a standard might require a certain approach to supporting the claim being made. |